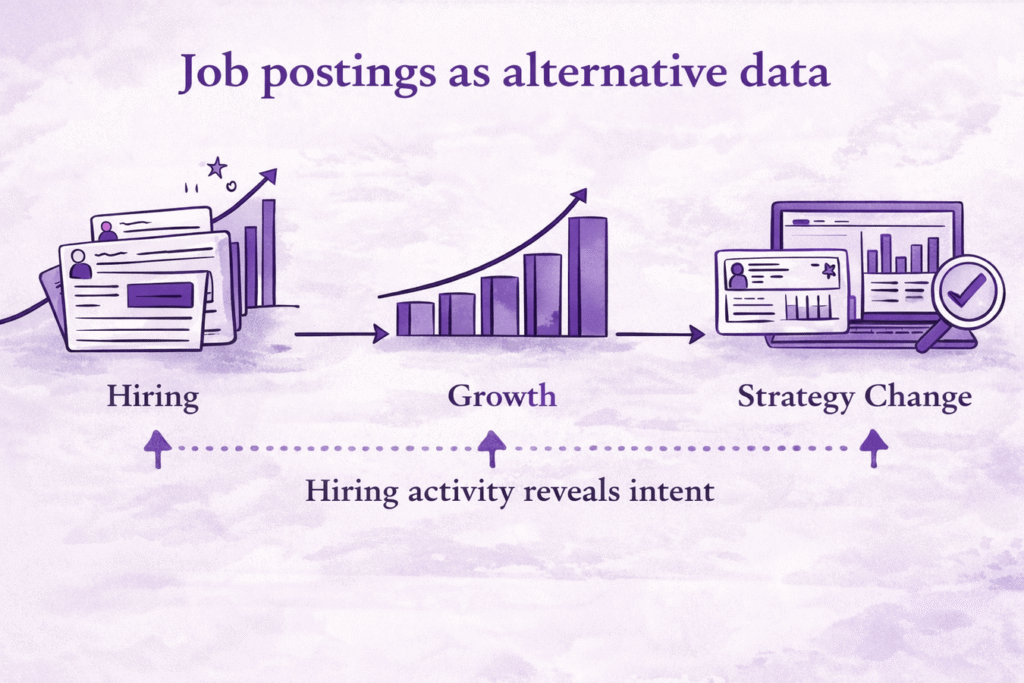
Finding companies that are actively hiring data engineers is more than a recruiting exercise—it’s one of the strongest indicators of organizational investment in data infrastructure, analytics, and scale.
For B2B sales teams, recruiters, and data vendors, data engineer hiring represents near-term intent. These roles are typically opened when a company is building or modernizing its data stack, supporting new products, or preparing for growth.
The challenge is accuracy and timing. Job boards are noisy, information goes stale quickly, and manual searches rarely capture sustained hiring behavior. This guide outlines a data-driven approach to identifying companies hiring data engineers using structured hiring signals and job data—turning fragmented postings into actionable intelligence.
The Challenge of Identifying Companies With Active Data Engineering Needs
At first glance, finding companies hiring data engineers seems straightforward: search job boards or LinkedIn and compile results. In practice, this approach breaks down as soon as you need scale, consistency, and signal quality.
Hiring signals are dynamic and fragmented across dozens of sources. Roles open and close quickly, titles vary widely, and postings are often poorly structured. Without normalization and historical context, it’s difficult to determine which companies have real, ongoing data engineering demand versus one-off or outdated listings.
Why job boards and manual searches fail at scale
Job boards are optimized for individual job seekers—not for analyzing hiring behavior across thousands of companies. Listings are frequently duplicated across platforms, mislabeled under generic engineering roles, or left open long after positions are filled.
Manual research introduces bias and blind spots. It misses private postings, smaller job boards, and international listings, and it provides no reliable way to track hiring trends over time. At scale, this results in incomplete coverage and inconsistent targeting.
The cost of outdated or incomplete hiring information for B2B teams
For B2B sales and marketing teams, acting on stale hiring data leads to wasted outreach and missed opportunities. Contacting companies after a hiring freeze—or before a real initiative begins—reduces conversion rates and undermines credibility.
Incomplete hiring data also prevents effective prioritization. Without knowing which companies are hiring aggressively versus casually, teams are forced to treat all accounts equally instead of focusing on those with urgent, budgeted needs.
Why Data Engineer Hiring Is a High-Intent Business Signal
Data engineering roles are rarely opportunistic hires. They are typically opened in response to concrete initiatives involving data platforms, analytics pipelines, machine learning, or operational scalability.
Unlike generic software engineering roles, data engineer hiring is closely tied to infrastructure decisions and long-term investment.
What data engineering roles indicate about company priorities
When a company hires data engineers, it often signals priorities such as:
- Building or migrating to centralized data warehouses
- Improving data quality, reliability, and pipelines
- Enabling analytics for decision-making across teams
- Supporting AI, machine learning, or advanced reporting use cases
These initiatives almost always require tools, services, and vendors—making data engineer hiring a strong proxy for purchasing intent.
How hiring velocity reflects growth and infrastructure investment
Hiring velocity adds critical context. A single data engineer opening may indicate maintenance or backfill, while multiple postings over several months suggest expansion or modernization.
Sudden increases in hiring often correlate with funding rounds, product launches, market expansion, or large-scale infrastructure changes. Consistency and acceleration are usually stronger signals than isolated spikes.
Relevance for B2B sales, recruiting, and data infrastructure vendors
Different teams use these signals in different ways:
- Recruiters identify companies with sustained demand and future hiring needs
- Sales teams target accounts entering an active buying cycle
- Data infrastructure vendors time outreach when budgets and urgency are highest
In all cases, data engineer hiring reduces guesswork and improves timing.
Step-by-Step Workflow to Find Companies Hiring Data Engineers
A structured workflow transforms raw job postings into reliable hiring signals. The goal is not just to find open roles, but to understand patterns, intent, and urgency at the company level.
Define data engineering roles, seniority, and scope
Start by defining what qualifies as a data engineering role. Common titles include:
- Data Engineer
- Analytics Engineer
- Platform Data Engineer
- Senior, Staff, or Principal Data Engineer
Decide whether to include adjacent roles such as machine learning engineers with heavy data infrastructure focus. Also determine which seniority levels matter—junior hires often signal team expansion, while senior hires may indicate architectural change.
Filter companies by active data engineer job openings
Next, focus only on active and recently updated job postings. Archived or stale listings introduce noise and false positives.
Company-level aggregation is critical here. One company with five concurrent data engineering openings is far more meaningful than five companies with a single outdated posting each.
Analyze hiring volume and velocity over time
Counts alone are not enough. Examine trends over time:
- Is data engineer hiring consistent month over month?
- Is the number of openings increasing?
- Are new roles appearing across multiple teams?
Sustained or accelerating hiring suggests long-term investment, while one-off spikes may reflect short-term projects.
Segment companies by geography, size, and industry
Segmentation aligns hiring signals with your go-to-market strategy:
- Geography affects compliance, data residency, and cloud choices
- Company size influences budget and buying cycles
- Industry reveals use-case complexity (e.g. fintech and healthcare have stricter data requirements than early-stage SaaS)
Prioritize accounts by urgency and consistency
Effective prioritization combines multiple factors:
- Number of data engineering roles
- Seniority of hires
- Hiring velocity and recency
- Cross-team hiring patterns
Companies hiring multiple senior data engineers simultaneously often have urgent, complex needs and higher willingness to engage with vendors or partners.
Validate hiring signals with complementary company activity
Hiring data is most powerful when validated against other signals such as:
- Funding announcements
- Cloud or data stack adoption
- Product launches
- Migrations or re-platforming initiatives
This context explains why a company is hiring—not just that it is.
How the Job Openings Dataset Supports This Workflow
A structured Job Openings Dataset makes this workflow repeatable and scalable. By normalizing, deduplicating, and time-stamping postings, it turns noisy job data into reliable hiring intelligence.
Detecting real-time data engineer postings at the company level
The dataset captures job postings as they appear across sources and maps them to the correct company entity. This enables near real-time visibility into which companies are actively hiring data engineers right now.
Filtering by role type, department, and seniority
Standardized role classifications allow teams to isolate true data engineering roles and separate them from generic software engineering. Seniority tags help distinguish foundational hiring from leadership or specialization hires.
Tracking hiring activity over time
Historical snapshots enable trend analysis, revealing whether hiring is accelerating, stable, or declining. This time-based view prevents misinterpretation of short-lived spikes or outdated roles.
Using hiring patterns as indicators of internal investment
When analyzed at scale, hiring patterns become proxies for internal investment. Companies increasing data engineer hiring often follow with higher spending on data platforms, tooling, and external services.
Common Mistakes When Searching for Companies Hiring Data Engineers
Even with access to job data, misinterpretation can undermine results. Avoiding common mistakes ensures hiring signals translate into meaningful action.
Relying on single postings without trend analysis
Single job postings lack context. Without historical data, it’s impossible to know whether a role represents a new initiative or routine backfill.
Confusing generic engineering roles with data-specific needs
Backend or full-stack roles do not necessarily indicate data investment. Accurate role classification is essential to avoid false assumptions.
Ignoring hiring slowdowns or freezes
A sudden drop in postings may signal budget constraints or shifting priorities. Ignoring these changes leads to mistimed outreach.
Treating hiring data as static
Hiring is dynamic. Treating job data as a static list instead of a time-based signal misses its real value: understanding momentum and change.
Conclusion: Using Hiring Signals to Identify High-Intent Companies
Companies hiring data engineers are often in the middle of transformation—building, scaling, or modernizing their data stack. When analyzed correctly, hiring signals provide one of the clearest windows into these initiatives.
Aligning hiring intelligence with B2B targeting
By integrating hiring intelligence into account selection and prioritization, B2B teams focus on companies with real, current needs. This alignment improves conversion rates, shortens sales cycles, and increases relevance.
Turning hiring signals into repeatable workflows
The key is moving from raw job postings to structured, time-based insights. With the right workflow and datasets, data engineer hiring becomes more than a list—it becomes a scalable signal for identifying high-intent companies at exactly the right moment.
Interested in finding out how PredictLeads Jobs dataset can help you out? Feel free to let us know! We’re here to help.