Most technographic data providers use similar detection techniques. However, the quality, accuracy, and freshness of the data can vary widely. Much of this difference depends on how providers collect and maintain their datasets.
In the previous section — “6 Best Technographic Data Providers in 2026” — we compared several platforms that offer technographic datasets. The main differences between these providers go beyond database size. Instead, they depend on the depth of detection systems, update frequency, and signal validation methods.
Some providers rely mainly on single-source website scraping. This approach can detect visible technologies on a website. However, it often misses deeper signals such as integrations, infrastructure changes, or emerging tool adoption.
Other providers take a broader approach. They combine several collection methods, which improves coverage and accuracy.
For example, these methods may include:
- large-scale website technology detection
- job posting analysis
- public integration signals
- developer ecosystem signals
- historical monitoring of technology changes
As a result, datasets built from multiple signal sources usually provide more reliable and complete technographic insights.

How PredictLeads Collects and Structures Technographic Data
PredictLeads collects technographic data by combining automated detection, structured signal processing, and continuous monitoring.
The Technologies Dataset and Technology Detections Dataset track technology adoption across millions of companies worldwide.
Instead of relying on a single detection method, PredictLeads combines several signals to build a more accurate view of company technology stacks.
These signals include the following.
Website Technology Detection
PredictLeads performs large-scale scans of company websites. These scans identify embedded scripts, frameworks, analytics tools, and infrastructure technologies.
For example, the system can detect technologies through:
- JavaScript libraries
- embedded tracking scripts
- analytics integrations
- front-end frameworks
As a result, PredictLeads can identify technologies used across marketing, analytics, payments, and developer environments.
Technology Usage Signals
In addition, PredictLeads analyzes signals across a company’s digital infrastructure. This includes marketing tools, analytics platforms, developer tools, and payment systems.
These signals help identify which technologies companies actively use in their operations.
Continuous Monitoring
Technology stacks change frequently. Therefore, PredictLeads continuously monitors technology detections.
This monitoring identifies when companies:
- adopt new tools
- remove technologies
- change infrastructure components
Consequently, PredictLeads tracks both current technology usage and historical technology changes. This allows users to see how company stacks evolve over time.
Where PredictLeads Stands Out
Many technographic providers focus only on technologies detected on websites.
PredictLeads takes a broader approach. It combines technographic signals with other company intelligence datasets. This approach allows users to connect technology adoption with broader company activity.
For example, technology detections can be analyzed together with the Job Openings Dataset – to see whether companies are expecting someone to understand technologies they use internaly. And Connections Dataset where we identify integrations or ecosystem partnerships
As a result, users move beyond simply identifying what technologies a company uses. Instead, they gain insight into why and when technology adoption occurs.

Technographic Data as Part of a Broader Company Intelligence System
Technographic data becomes far more valuable when combined with other company intelligence signals.
For example, consider a company that:
- recently raised funding
- hires engineers with experience in a specific technology
- adopts new infrastructure tools
Together, these signals may indicate a product expansion or scaling phase.
PredictLeads enables this type of analysis by structuring technographic data alongside hiring, funding, news, and ecosystem signals.
Therefore, users can do more than identify technology stacks. They can also understand company growth patterns, product development activity, and strategic direction.
What This Means for Technographic Data Users
For teams working in sales intelligence, market research, or investment analysis, the key question is not only which technologies companies use. Instead, the critical factor is how accurately and frequently these technologies are detected and updated.
Providers that combine multiple signal sources and maintain continuous monitoring typically deliver more reliable datasets.
PredictLeads focuses on structured, continuously updated company intelligence signals. These signals help users analyze technology adoption within the broader context of company behavior.
In the next section, we will explore how businesses use technographic data in practice. Specifically, we will examine how teams apply these signals to sales prospecting, competitive intelligence, and market analysis.
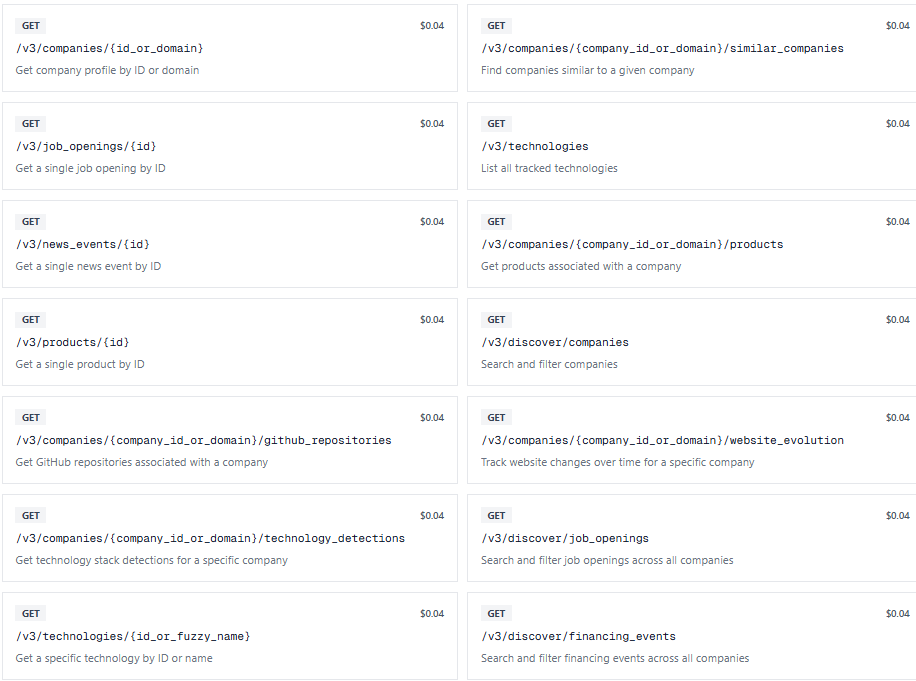
Get Technographic Data Through the PredictLeads API
If you want to track technology adoption across companies, PredictLeads provides technographic data and you can access it both through APIs or flat files.
With PredictLeads, you can:
- identify which technologies companies use
- detect new technology adoption across markets
- monitor changes in company technology stacks over time
- combine technographic signals with hiring, funding, and news events
As a result, teams can build workflows for sales prospecting, competitive intelligence, market research, and investment analysis.
You can explore the PredictLeads API documentation here:
https://docs.predictleads.com/v3
Alternatively, you can learn more about the available datasets and how they help detect technology adoption across millions of companies.